
- Introduction:
In the workplace, violence is a serious problem that poses a risk to many people. It includes things such as hitting, yelling, bullying, and even scary things like terrorism. While we try our best to make work a safe and pleasant place, violence still occurs quite often and hurts many people as a result. It can happen between coworkers, or even from people outside the company, such as customers or visitors.
The problem with workplace violence is that it takes away people’s rights and makes them feel unsafe. Work is supposed to be a safe and respectful place, with everyone feeling valued and protected, but workplace violence abuses that.
It is my intention in this introduction to provide you with an overview of workplace violence and how it affects people. In this introduction we will discuss what it is, why it occurs, and how it affects the people and will go over how you can recognize workplace violence, prevent it from occurring, and keep all employees safe at work. If we understand the problems with better understanding of this problem then it will enable us to work together to improve the workplace and make it a safer and happier and more productive place to work.
- Overview of Workplace Violence:
Workplace violence is when someone at work is treated badly or hurt by someone else. It can happen in many ways, like hitting, yelling, bullying, or even threatening with weapons. This kind of violence is a big problem because it makes people feel scared, stressed, and unsafe at work.
2.1 Why Does Workplace Violence Occur?
There are many reasons why workplace violence happens. Sometimes, it’s because people are stressed, angry, or unhappy with their jobs. Other times, it’s because they have problems outside of work that they bring with them. Sometimes, it’s because they don’t know how to solve problems without using violence. And sadly, there are also people who intentionally want to harm others.
2.2 How Does Workplace Violence Affect People?
Workplace violence can have a big impact on people’s lives. It can make them feel scared, anxious, and depressed. Victims may suffer physical injuries, like bruises or broken bones, or they may experience emotional trauma, such as anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It can also affect people’s ability to work, their relationships with coworkers, and their overall well-being.
People who experience workplace violence may have trouble sleeping, concentrating, or doing their job well. It can also make them feel like they can’t trust others or be safe at work.
2.3 How Can We Recognize Workplace Violence?
It’s important to be able to recognize the signs of workplace violence so that it can be addressed before it escalates. Some warning signs include:
- Physical aggression, like hitting, pushing, or throwing things, cuts, or injuries that can’t be explained.
- Verbal aggression, such as shouting, cursing, or making threats, hearing yelling, threats, or insults directed at someone else.
- Emotional signs: Feeling scared, anxious,sexual harassment or upset at work.
- Intimidating behavior, like invading personal space or making menacing gestures.
- Bullying or harassment, including teasing, spreading rumors, or singling out individuals.
- Behavioral signs: Changes in behavior or mood, Acting differently than usual,like becoming withdrawn, anxious, or irritable, avoiding certain people or places at work.
- Increased absenteeism or unexplained injuries.
Recognizing workplace violence is important so we can stop it and help those who are affected.

3. Cause of Workplace Violence:
Workplace violence can happen for many reasons, and it’s important to understand what causes it so we can work together to prevent it. Here are some common causes of workplace violence:
- Stress, Anger and Frustration: Sometimes, people bring their stress and anger from outside of work into the workplace. This can happen if they’re dealing with problems at home, financial troubles, or health issues. When people are stressed or angry, they may lash out at their coworkers or act aggressively.
- Conflict and Disputes: Workplaces are full of different people with different opinions and personalities, which can sometimes lead to conflicts and disputes. If these conflicts aren’t resolved peacefully, they can escalate into violence. This might happen if someone feels disrespected, ignored, or unfairly treated.
- Poor Communication: When communication breaks down in the workplace, misunderstandings can occur, and tensions can rise. If people don’t feel heard or valued, they may become frustrated and resort to aggressive behavior to get their point across.
- Bullying and Harassment: Bullying and harassment in the workplace can create a toxic environment where people feel intimidated or threatened. This behavior can come from coworkers, supervisors, or even clients or customers.
- Job Insecurity: Fear of losing one’s job or facing layoffs can create anxiety and tension among employees. This insecurity may lead to heightened emotions and conflicts in the workplace.
- Personal Problems: People may bring their personal problems to work, such as financial difficulties, relationship issues, or mental health struggles. These problems can affect their behavior and interactions with others.
- Substance Abuse: Unfortunately, some people may struggle with substance abuse issues, such as drugs or alcohol. Substance abuse can impair judgment and behavior, making it more likely for someone to act violently in the workplace.
- Unresolved Issues: If workplace issues like discrimination, harassment, or bullying are not addressed properly, they can create a toxic environment where violence becomes more likely. People may feel powerless or trapped in these situations, leading to feelings of anger or resentment.
- Lack of Policies and Training: If workplaces don’t have clear policies or training on how to handle conflicts and prevent violence, it can make it easier for violence to occur.
- Poor Management Practices: In some cases, poor management practices, such as favoritism, micromanagement, or lack of support, can contribute to workplace violence. When employees feel undervalued or mistreated by their supervisors, they may become disillusioned and more prone to aggressive behavior.
- Lack of Policies and Training:Inadequate workplace policies and training on conflict resolution, communication, and violence prevention can contribute to a culture where violence is more likely to occur.
- External Factors: Sometimes, workplace violence may be triggered by external factors, such as economic downturns, layoffs, or changes in company policies. These events can create uncertainty and anxiety among employees, which may manifest in aggression or violence.
By understanding these common causes of workplace violence, we can take proactive steps to identify potential risks and take proactive measures to prevent workplace violence. By addressing them can create a safer, more harmonious & positive work environment for everyone. This includes promoting open communication, conflict resolution strategies, and supportive management practices, as well as providing resources and support for employees dealing with personal issues or substance abuse. Together, we can work towards preventing workplace violence and fostering a culture of respect and cooperation in the workplace.

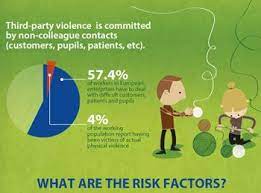
4. Risk Factors of Workplace Violence:
It is important to understand that risk factors are things that can increase the likelihood of something bad happening. In the case of workplace violence, there are several risk factors that make it more likely to occur. Here are some common risk factors:
- High-Stress Environments: Jobs that are high-pressure or demanding can create stress for employees, making them more likely to get frustrated or angry and lash out at coworkers.
- Poor Communication: When people at work don’t communicate well with each other, misunderstandings can happen, and tensions can rise. This can lead to conflicts and, in some cases, violence.
- Unresolved Conflicts: If there are ongoing disputes or conflicts between coworkers that haven’t been resolved, they can escalate and turn into violence. It’s important to address conflicts early and find peaceful solutions.
- Absence of the motivation of Teamwork/ Team building: Due to non-communicate well with each other, misunderstandings can happen, and tensions can rise and unresolved conflicts can lead to demotivate personnels. unfortunately they would be unable to work as a team.
- Substance Abuse: Sometimes, people who use drugs or alcohol may behave aggressively or unpredictably, putting themselves and others at risk of violence.
- Lack of Support: Employees who feel unsupported or mistreated by their supervisors or coworkers may become frustrated or resentful, increasing the likelihood of aggressive behavior.
- Working Alone or in Isolation: People who work alone or in isolated areas may be more vulnerable to violence because there’s nobody around to help or witness what’s happening.
- History of Violence: If there have been previous incidents of violence in the workplace, it increases the risk that it can create a culture of fear and tension, and could happen again in the future.
- External Factors: Changes in the economy, company layoffs, or other external events can cause stress and uncertainty among employees, which may lead to increased aggression or violence.
By understanding these risk factors and taking steps to address them, we can help prevent workplace violence and create safer, more supportive work environments for everyone. This includes promoting good communication, providing support for employees dealing with stress or substance abuse, and fostering a culture of respect and cooperation in the workplace.
Impacts of workplace violence:
1. Physical and Mental Health Effect : When bad things happen at work, people can get hurt physically, like getting bruises or cuts, or even really bad injuries. It can also make people feel bad in their minds for a long time, like having aches and pains that won’t go away or feeling really scared or upset all the time. This can make it hard for people to focus or feel good overall.
2. Productivity and Morale If people don’t feel safe at work, they won’t feel happy or motivated to do their best. They might feel stressed out, scared, or not interested in their work anymore. When violence happens or people hear about it, it makes everyone feel worried and tense, which can make it hard to work together and get things done.
3. Loss of Trust and Confidence : When violence happens at work, it makes people feel like they can’t trust their bosses or the company to keep them safe. They might not feel confident that things will get better, which can make it hard for everyone to talk to each other and work together well.
4. Increased Absenteeism and Turnover : If someone gets hurt or feels scared at work because of violence, they might need to take time off to get better or might even quit their job because they don’t feel safe. This means more people missing work and leaving their jobs, which makes it harder for the company to get things done and costs them more money to find new people and train them.
5. Legal and Financial Costs : Violence at work can cause big problems for the company, like getting sued or having to pay money for people’s injuries or suffering. They might have to pay for medical bills, lawyers, and settlements, and their insurance costs could go up too.
6. Damage to Reputation : If people hear about violence happening at a company, they might not want to do business with them anymore. This can make the company lose customers, investors, and partners, which means less money coming in and a bad reputation that’s hard to fix.
7. Decreased Productivity : When people feel scared or stressed at work because of violence, they won’t be able to concentrate or do their jobs well. They might spend more time worrying about their safety instead of getting their work done, which slows everything down.
8. Disruption of Business Operations : Violence at work can mess up how things normally get done. It takes time and resources to investigate what happened, deal with people being absent, and put in new safety measures. This means the company might not be able to focus on their main tasks and goals like they should.
9. Impact on Employee Relationships : When violence happens at work, it can make people not trust each other anymore. They might feel scared or blame their bosses for not stopping it, which can make it hard for everyone to work together and feel like a team.
10. Long-term Organizational Consequences : The effects of violence at work can last a long time for a company. It can take a while to build back trust, make people feel happy and motivated again, and get things back to normal. The company might also have to follow stricter rules and spend more money on safety measures, which can affect how they do business in the future.
Overall, workplace violence has multifaceted impacts that extend beyond immediate physical harm. It affects the mental health and well-being of individuals, undermines organizational culture and productivity, and poses significant financial and reputational risks for businesses. Addressing workplace violence requires a comprehensive approach that prioritizes prevention, intervention, and support for victims and employees.

Prevention and Managing Plan for Workplace Violence:
1. Promote Respectful Communication:
– Encourage employees to communicate openly and respectfully with each other.
– Provide training on effective communication skills to help prevent misunderstandings and conflicts.
2. Establish Clear Policies and Procedures:
– Develop clear policies and procedures that explicitly prohibit workplace violence, harassment, and bullying.
– Ensure all employees are aware of these policies and understand the consequences of violating them.
3. Provide Training and Education:
– Offer training sessions on recognizing the signs of potential violence and how to de-escalate tense situations.
– Educate employees on the importance of reporting any incidents of workplace violence promptly and confidentially.
4. Create Support Systems:
– Establish support systems for employees who experience or witness workplace violence, including access to counseling or employee assistance programs.
– Ensure confidentiality and provide resources for victims to seek help and support.
5. Enhance Security Measures:
– Implement security measures such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and security personnel to deter violence and ensure a safe work environment.
– Conduct regular security assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
6. Foster a Positive Work Environment:
– Promote a positive work culture based on mutual respect, trust, and collaboration.
– Recognize and reward positive behavior and contributions to create a supportive and inclusive workplace.
7. Address Employee Concerns Promptly:
– Encourage employees to report any concerns or grievances they may have, and take them seriously.
– Investigate and address reported incidents of workplace violence promptly and impartially.
8. Encourage Conflict Resolution:
– Provide training on conflict resolution techniques and encourage employees to resolve conflicts peacefully and constructively.
– Offer mediation services or other dispute resolution mechanisms to help employees address conflicts.
9. Regularly Review and Update Policies:
– Regularly review and update workplace violence prevention policies to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
– Solicit feedback from employees and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
10. Promote Awareness and Education:
– Raise awareness about workplace violence through training sessions, workshops, and informational materials.
– Educate employees on the impact of workplace violence and the importance of prevention efforts to create a safe and healthy work environment.

Legal Considerations and Reporting Procedures for Workplace Violence in India:
1. Indian Penal Code (IPC):
– The IPC prohibits various forms of violence, including assault, intimidation, and harassment, which are punishable under criminal law.
2. Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act:
– This Act lays down rules governing the conditions of employment in industrial establishments.
– It may include provisions related to disciplinary actions for acts of violence in the workplace.
3. Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013:
– This Act aims to prevent and address cases of sexual harassment at the workplace.
– It mandates the establishment of Internal Complaints Committees (ICCs) to handle complaints and ensure redressal.
4. Vishaka Guidelines:
– These guidelines were established by the Supreme Court of India in the Vishaka v. State of Rajasthan case.
– They provide guidelines for preventing and addressing sexual harassment at the workplace until the enactment of the Sexual Harassment Act.
5. Reporting Procedures:
– Employees who experience or witness workplace violence should report it immediately to their employer, HR department, or designated authority.
– The report should include details of the incident, such as date, time, location, and individuals involved.
6. Internal Complaints Committee (ICC):
– Employers are required to set up ICCs to receive and address complaints of workplace violence, including sexual harassment.
– ICCs are responsible for conducting inquiries, providing support to victims, and recommending appropriate action.
7. Confidentiality and Protection:
– Employers must ensure confidentiality and protect the identity of employees who report incidents of workplace violence.
– Employees who report workplace violence should not face retaliation or adverse consequences for filing complaints.
8. Investigation and Action:
– Employers are obligated to conduct a fair and impartial investigation into reported incidents of workplace violence.
– If the allegations are substantiated, appropriate disciplinary action should be taken against the perpetrator.
9. Legal Recourse:
– Employees have the right to seek legal recourse under Indian laws if they experience workplace violence.
– They can file complaints with the appropriate authorities or seek legal advice to pursue civil or criminal action against the perpetrator.
10. Awareness and Training:
– Employers should provide training and awareness programs to employees on their rights and responsibilities regarding workplace violence.
– Training should cover topics such as recognizing signs of violence, reporting procedures, and available support services.
11. Compliance with Regulations:
– Employers must ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations related to workplace violence.
– Failure to comply with legal requirements can result in penalties, fines, or legal action against the organization.
12. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
– Employers should continuously monitor and review their policies and procedures for preventing and addressing workplace violence.
– Regular audits and assessments should be conducted to identify areas for improvement and ensure a safe and healthy work environment for all employees.
Guidelines for Level Consideration and Reporting Procedures for Workplace Violence According to ILO, OSHA, and European Union Standards:
1. Recognize Signs of Workplace Violence:
– Learn to identify behaviors like aggression, threats, intimidation, or harassment in the workplace, as outlined by the International Labour Organization (ILO), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and the European Union (EU).
– Be vigilant and observant of any unusual or concerning behavior exhibited by coworkers or supervisors.
2. Assess the Severity of the Situation:
– Evaluate the seriousness and potential risk of the situation before taking any action, considering factors such as the nature of the behavior, the history of individuals involved, and immediate safety concerns.
3. Report Immediately:
– If you witness or experience workplace violence, report it promptly to your supervisor, HR department, or designated authority, in accordance with ILO, OSHA, and EU guidelines.
– Follow the established reporting procedures outlined in your organization’s policies and procedures.
4. Provide Detailed Information:
– When reporting workplace violence, provide detailed information about the incident, including the date, time, location, and individuals involved.
– Describe the behavior or actions observed and any impact it had on you or others, following the reporting guidelines set forth by ILO, OSHA, and the EU.
5. Maintain Confidentiality:
– Respect the confidentiality and privacy of individuals involved in workplace violence incidents, as emphasized by ILO, OSHA, and EU standards.
– Avoid disclosing sensitive information to unauthorized individuals and refrain from discussing incidents with colleagues unless necessary.
6. Seek Support:
– If you are a victim of workplace violence, seek support from your employer, HR department, or employee assistance program, in line with ILO, OSHA, and EU regulations.
– Take advantage of available resources, such as counseling services or support groups, to address any emotional or psychological impact.
7. Cooperate with Investigations:
– If an investigation is conducted into a workplace violence incident, cooperate fully with the process as outlined by ILO, OSHA, and EU guidelines.
– Provide any relevant information or evidence that may help resolve the situation and prevent future incidents.
8. Follow Up:
– Follow up on reported incidents to ensure that appropriate action is taken and necessary measures are implemented to prevent recurrence, in accordance with ILO, OSHA, and EU standards.
– Stay informed about the progress of investigations and any disciplinary actions taken against perpetrators.
9. Advocate for Prevention:
– Advocate for proactive measures to prevent workplace violence, such as training programs, awareness campaigns, and policy revisions, as recommended by ILO, OSHA, and EU guidelines.
– Work collaboratively with management and colleagues to create a safe and respectful work environment for all employees.
10. Stay Vigilant:
– Remain vigilant and alert to your surroundings, and report any concerns or suspicions of workplace violence promptly, in accordance with ILO, OSHA, and EU standards.
– Encourage a culture of reporting and accountability within your organization to prevent workplace violence and ensure the safety and well-being of everyone.
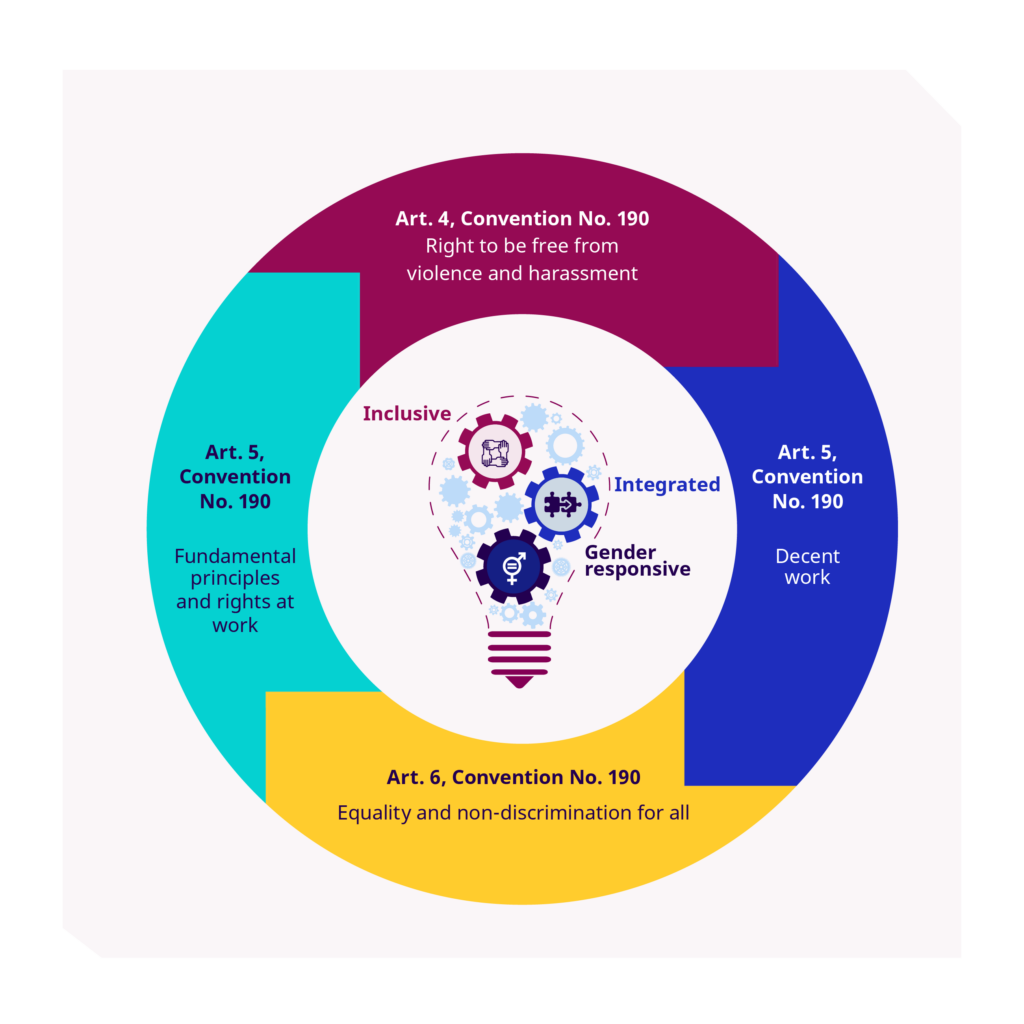
The International Labour Organization (ILO) has not published specific guidelines solely focused on workplace violence under a single rule or convention. However, the ILO addresses the issue of workplace violence and harassment through various instruments and conventions, including the “Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190).”
The ILO’s Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190), is a significant instrument that addresses workplace violence and harassment comprehensively. It defines violence and harassment as behaviors, threats, or actions that harm or intimidate workers, and it requires governments, employers, and workers to take steps to prevent and address these issues.
In easy language, Convention No. 190 sets out rules and recommendations to ensure that every worker has the right to a workplace free from violence and harassment. Here are some key aspects of the convention:
1. Government Responsibility:
– Governments are responsible for adopting laws and regulations to prohibit workplace violence and harassment.
– They must promote awareness and education on these issues and ensure that effective measures are in place to prevent and address them.
2. Employer Duties:
– Employers are required to create a safe work environment where violence and harassment are not tolerated.
– They must develop and implement policies and procedures to prevent these behaviors, provide training to employees, and establish mechanisms for reporting and addressing incidents.
3. Worker Rights:
– Workers have the right to report incidents of violence and harassment without fear of retaliation.
– They should receive support and assistance if they experience these behaviors and should have access to remedies if their rights are violated.
4. Scope of Protection:
– The convention covers all workers, regardless of their employment status or type of work they perform.
– It applies to both the formal and informal sectors and to workers in all industries and occupations.
Overall, Convention No. 190 aims to create a culture of respect and dignity in the workplace, promoting equality and ensuring that all workers can perform their jobs without fear of violence or harassment. While it does not provide specific guidelines for workplace violence alone, it forms a crucial part of the ILO’s efforts to address this issue globally.
Resources for Workplace Violence Prevention in India:
Workplace violence is a significant concern in India, and various resources are available to support employers, employees, and other stakeholders in preventing and addressing this issue. These resources encompass legal frameworks, government initiatives, training programs, support services, and collaborative efforts aimed at promoting a safe and respectful work environment. Here’s a detailed overview of resources for workplace violence prevention as per Indian laws:
1. Legal Framework:
– The primary legal framework for workplace violence prevention in India includes laws such as the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, the Factories Act, 1948, and the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013.
– These laws provide guidelines and regulations for employers to ensure the safety, health, and well-being of employees, including measures to prevent and address workplace violence.
2. Government Initiatives:
– The Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India, implements various initiatives to promote workplace safety and prevent violence.
– Government agencies such as the Directorate General of Factory Advice Service and Labour Institutes (DGFASLI) provide guidance, training, and resources on occupational safety and health, including strategies for preventing workplace violence.
3. Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Training Programs:
– Several organizations, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private training providers, offer OSH training programs that cover workplace violence prevention.
– These programs educate employers and employees on recognizing, preventing, and responding to workplace violence incidents, emphasizing legal obligations, risk assessment, and mitigation strategies.
4. Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs):
– Some employers in India offer Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) to support employees’ mental health and well-being, including resources for dealing with workplace violence.
– EAPs may provide counseling services, crisis intervention, stress management, and referrals to external support services for employees affected by workplace violence.
5. Legal and Compliance Resources:
– Legal firms specializing in employment law and labor regulations in India offer guidance on legal requirements related to workplace violence prevention.
– These resources may include legal updates, interpretations of relevant laws and regulations, compliance checklists, and assistance with policy development tailored to Indian laws.
6. Research and Publications:
– Academic institutions, research organizations, and industry associations in India conduct studies and publish reports on workplace violence prevalence, causes, and prevention strategies.
– These research findings and publications provide valuable insights for employers and organizations to inform their prevention efforts and tailor interventions to address specific risks and challenges in the Indian context.
7. Collaboration and Advocacy:
– Collaboration between government agencies, employers, trade unions, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and civil society plays a crucial role in advancing workplace violence prevention efforts in India.
– Collaborative initiatives aim to share resources, exchange best practices, advocate for policy changes, and raise awareness about workplace violence and its impact on employees and organizations.
Overall, leveraging these resources and partnerships is essential for employers and organizations in India to effectively prevent and address workplace violence, comply with legal requirements, and promote a safe and respectful work environment for all employees.
Resources for Workplace Violence Prevention As Per International Standards:
Workplace violence prevention is a critical priority for employers and organizations to ensure the safety and well-being of their employees. To effectively address this issue, various resources are available to support and guide employers, workers, and other stakeholders in implementing prevention strategies and creating a safe work environment. These resources encompass a wide range of tools, materials, training programs, and support services aimed at preventing, mitigating, and responding to workplace violence incidents.
1. Government Agencies:
– Many government agencies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, provide comprehensive resources on workplace violence prevention.
– These resources include guidelines, fact sheets, training materials, and compliance assistance to help employers understand their legal obligations and implement effective prevention measures.
2. Non-Profit Organizations:
– Non-profit organizations dedicated to workplace safety and employee well-being often offer valuable resources on workplace violence prevention.
– These organizations may provide training programs, educational materials, research reports, and best practice guides tailored to specific industries or sectors.
3. Professional Associations:
– Professional associations in fields such as human resources, security, healthcare, and education frequently offer resources on workplace violence prevention.
– These resources may include webinars, conferences, workshops, and certification programs designed to enhance knowledge and skills in preventing and managing workplace violence.
4. Training Programs:
– Various training programs are available to help employers and employees recognize, prevent, and respond to workplace violence.
– These programs may cover topics such as conflict resolution, de-escalation techniques, threat assessment, emergency response, and post-incident support.
5. Online Portals and Toolkits:
– Online portals and toolkits curated by government agencies, non-profit organizations, and industry associations serve as centralized repositories of workplace violence prevention resources.
– These portals may offer downloadable materials, interactive training modules, case studies, assessment tools, and links to additional resources.
6. Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs):
– Many employers provide Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) to support employees’ mental health and well-being, including resources for dealing with workplace violence.
– EAPs may offer counseling services, crisis intervention, stress management, and referrals to external support services for employees affected by workplace violence.
7. Legal and Compliance Resources:
– Legal and compliance resources, such as legal firms specializing in employment law and labor regulations, can provide guidance on legal requirements related to workplace violence prevention.
– These resources may include legal updates, interpretations of relevant laws and regulations, compliance checklists, and assistance with policy development.
8. Research and Publications:
– Academic research, industry studies, and publications by thought leaders provide valuable insights into the prevalence, causes, consequences, and prevention strategies of workplace violence.
– Employers and organizations can leverage these resources to inform their prevention efforts and tailor interventions to address specific risks and challenges.
9. Support Services:
– In addition to preventive measures, employers should ensure access to support services for employees who have experienced or witnessed workplace violence.
– These services may include counseling, trauma-informed care, victim advocacy, legal assistance, and peer support groups to help individuals cope with the aftermath of violence incidents.
10. Collaborative Initiatives:
– Collaborative initiatives involving government agencies, employers, unions, advocacy groups, and community organizations play a crucial role in advancing workplace violence prevention efforts.
– By working together, stakeholders can share resources, exchange best practices, and advocate for policy changes to address systemic issues contributing to workplace violence.
Overall, a comprehensive approach to workplace violence prevention requires leveraging a diverse array of resources and partnerships to address the complex nature of this issue effectively. By investing in prevention efforts and creating a supportive and proactive workplace culture, employers can mitigate risks, protect employees, and promote a safer and healthier work environment for all.
Conclusion:
To sum up, workplace violence is a big problem that includes physical, verbal, and mental abuse. It’s important to prevent it because having a safe and respectful workplace is really important for everyone’s happiness and ability to work well.
There are different types of workplace violence like hitting, yelling, or making someone feel bad on purpose. It’s important to understand why it happens, like if there’s a lot of stress or if the company doesn’t have good rules in place.
Workplace violence doesn’t just hurt people physically. It can also make them feel bad mentally, make it hard for them to work, and make the company look bad. So, it’s important to have plans to stop it from happening. This includes having good rules, making sure the workplace is safe, and making sure everyone is treated nicely.
It’s also important to know what to do if something bad happens. There are rules and laws that say what should happen, and there are places to get help and support.
